Being diagnosed with gestational diabetes can leave an expectant mother anxious and frustrated. Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) refers to the symptoms of high blood sugar that first occur or are detected during pregnancy. According to statistics, its incidence rate among pregnant women worldwide is approximately 15%, meaning that many mothers will experience similar challenges. [1]
But don't worry, with effective gestational diabetes management, most mothers with GDM can effectively control their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
So, how to manage gestational diabetes for pregnant women? The key lies in monitoring, diet, exercise, and medical intervention when necessary. Continue reading to learn more.
Blood Glucose Level Monitoring
How to manage gestational diabetes? Starts with consistent and accurate blood glucose monitoring, as it guides the adjustments to your blood sugar control plan.
1. Blood Glucose Control Targets
According to the British Diabetic Association, the reference ranges of normal blood sugar for pregnant women are: [2]
- A fasting plasma glucose < 95 mg/dL (5.3 mmol/L)
- A one-hour postprandial glucose level < 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L)
- A two-hour postprandial glucose level < 115 mg/dL (6.4 mmol/L)
2. Using Blood Glucose Monitors
How to monitor blood glucose? The blood glucose monitor (BGM) is a traditional and useful tool for blood glucose monitoring, providing accurate and rapid measurements, which was recommended by the British Diabetic Association as a convenient monitoring solution.
BGM devices measure glucose concentration based on the electrochemical method. The glucose in the blood sample can react with glucose oxidase on the test strip, generating a weak current. This current’s strength is proportional to the glucose concentration and is measured by the device’s internal chip. How it works:
- Prepare the blood glucose monitor, test strips, lancets, alcohol swabs, and cotton swabs. Insert the test strip into the monitor.
- Disinfect your fingertip with an alcohol swab, then use a disposable lancet to quickly puncture the skin.
- Wipe away the first blood drop with a clean tissue, then gently touch the second drop to the test strip, avoiding contamination.
- The BGM will display your blood glucose reading. Use a cotton swab to stop the bleeding, then dispose of the used lancet and test strip in a designated container.
Ensure the entire process is completed within 3 minutes to ensure more accurate test results.
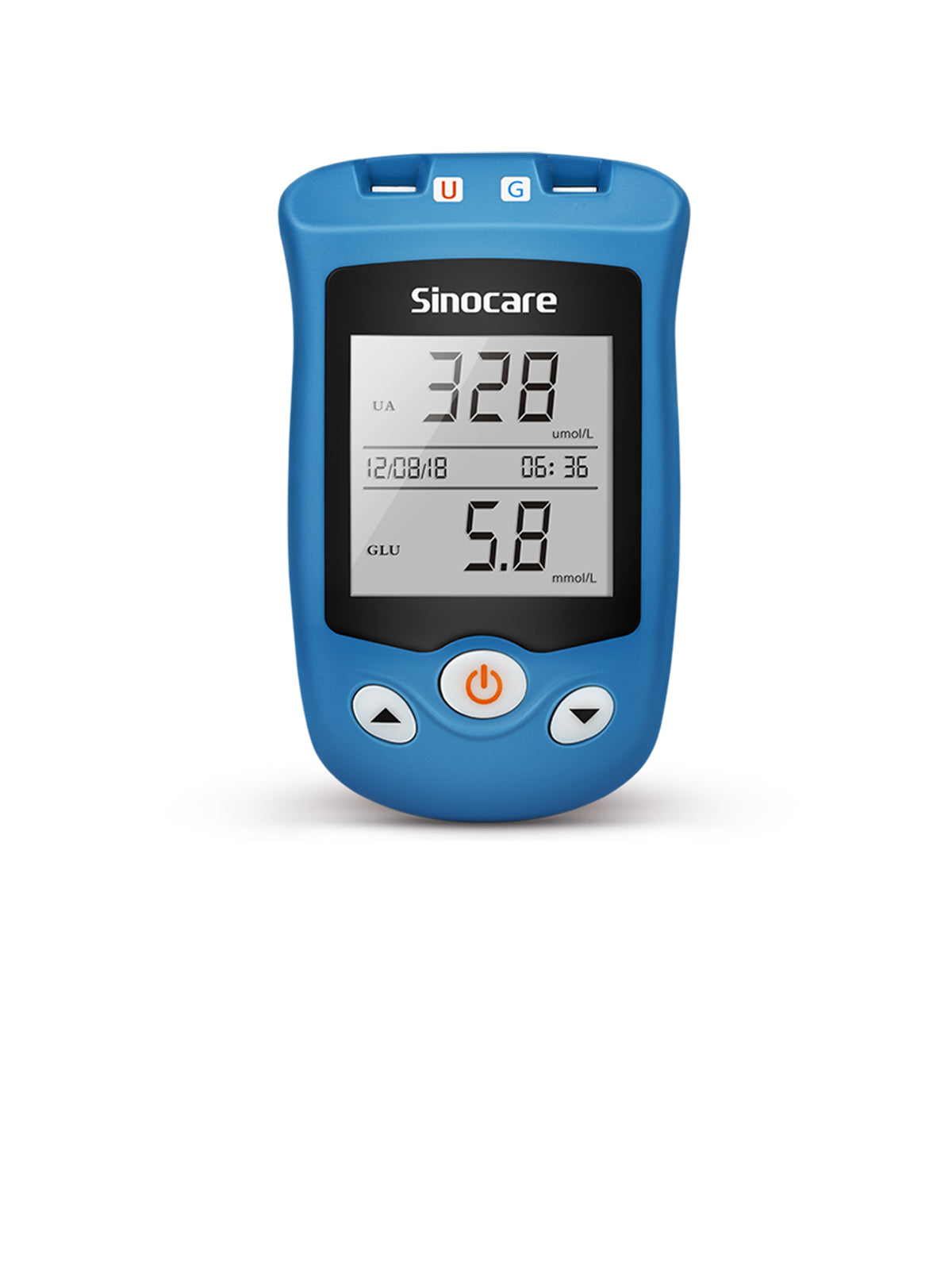
The BGM can record test results over multiple days. For example, the Sinocare Safe AQ Pro I can display the overall, pre-meal, and post-meal average glucose values of 7/14/30/90 days, helping you better understand your glucose trends.
Healthy Diet for Gestational Diabetes
How to manage gestational diabetes for pregnant women? The most important thing is to adjust the diet. These carefully curated diet diabetes pregnancy tips help maintain stable blood glucose levels while meeting the nutritional needs of both the mother and the fetus.
1. Eat Meals on Time
Eating at regular intervals helps prevent significant blood sugar fluctuations.
This means you should never skip a meal, control your food portions, and distribute your daily food intake across three main meals and 2-3 snacks.
This can effectively prevent postprandial hyperglycemia and pre-meal hypoglycemia. Additionally, a bedtime snack containing high-quality protein and complex carbohydrates can slowly release energy during the night, helping to prevent nocturnal hypoglycemia.
2. Choose High-quality Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Healthy Fats
To achieve a healthy diet for gestational diabetes, the focus lies on quality. The American Diabetes Association recommends a dietary reference intake of at least 175g of carbohydrates (approximately 35% of a 2,000-calorie diet), at least 71g of protein, and 28g of fibre for all pregnant individuals. [3]
First, choose high-quality carbohydrates. These foods are digested and absorbed slowly, with a low glycemic index. For example:[4]
- Instead of white bread, opt for high-fibre whole grains (such as whole wheat bread, rye bread, oats, brown rice), legumes (such as chickpeas, beans, lentils), and most vegetables (leafy greens, broccoli, etc.).
- Fruits should be low-GI varieties (such as apples, pears, grapefruit, peaches) and consumed between meals. Avoid smoothies and fruit juices.
- If you eat dairy products, ensure they are sugar-free.
Second, ensure adequate intake of protein, which is essential for a balanced diet and has minimal impact on blood sugar. Examples include lean meats, poultry, fish, and eggs.
Finally, include healthy fats from sources such as nuts, avocados, and seeds. Focus on unsaturated fats and remember to avoid trans fats.
The dietary choices mentioned above are all beneficial for individuals with pregnancy diabetes. However, with so many options available, how should they be combined? This is where the "food exchange portion" method becomes particularly useful.
3. Food Exchange Portion Method
The food exchange portion method groups foods that provide similar calories and nutrients into "one portion." People with diabetes can simply swap foods within the same category instead of calculating the nutrients in each individual food. [5]
The method primarily focuses on the carbohydrate, protein, fat, and calorie content per portion. Since each portion can consist of various foods, you have multiple pairing options without worrying about eating the same foods repeatedly. What to eat with gestational diabetes? The following are recommended food exchange lists by the American Diabetes Association:[5]
Starch/Bread List
|
Food |
Serving size |
|
Bulgur (cooked) |
1/2 cup |
|
Cooked cereals |
1/2 cup |
|
Grape Nuts |
3 tbsp |
Vegetables
|
Food (raw) |
Serving size |
|
Greens (collard, mustard, turnip) |
1 cup |
|
Leeks |
1 cup |
|
Pea pods |
1 cup |
Fruit
|
Food |
Serving size |
|
Apples |
1 |
|
Banana |
1/2 |
|
Cherries |
12 whole |
Skim Milk
|
Food |
Serving size |
|
Skim milk |
1 cup |
|
Plain nonfat yogurt |
8 oz |
4. Be Cautious of “Hidden Sugars”
Many processed foods, sauces, and beverages contain added sugars that can cause unexpected spikes in glucose levels.
Ingredients to be cautious of include white sugar, high-fructose corn syrup, maltose, honey, concentrated fruit juice, etc. They are commonly found in foods such as milk tea, ketchup, salad dressings, and flavoured yoghurt. Whenever possible, choose fresh, whole foods over processed options.
5. Small, Frequent Meals and a Bedtime Snack
Instead of large meals, smaller and more frequent portions help avoid big fluctuations in blood glucose. Including a light snack before bedtime, such as a serving of whole-grain crackers with a small portion of protein, can help prevent overnight hypoglycemia.
Lastly, exact food needs vary and should be confirmed with a healthcare provider.
Safe Exercise is Also Essential
For gestational diabetes management, a healthy diet and safe exercise are both indispensable.
1. Benefits of Exercise
Regular, moderate exercise not only directly helps control normal blood sugar for pregnant women but also contributes to overall physical health.
Exercise helps burn excess calories, improves blood circulation, and alleviates common pregnancy-related issues such as lower back pain and oedema. Plus, it can also relieve stress, anxiety, and depression during pregnancy and enhance sleep quality.
2. Recommended Exercise
For pregnant women, only low-impact exercise for pregnancy diabetes is recommended. Walking is a simple and safe choice that can be incorporated into daily routines. Prenatal yoga supports flexibility, posture, and relaxation, while swimming is gentle on the joints and effective for maintaining cardiovascular fitness.
Intense exercises that involve running, jumping, heavy lifting, contact sports, or diving should be avoided, as they may increase the risk of injury or stress.
3. Safety Guidelines
While exercising, take care of the following safety precautions:
- Optimal timing: Engaging in exercise about 30 to 60 minutes after meals can help the body use post-meal glucose more effectively.
- Intensity and duration: Aim for moderate-intensity activity, such as brisk walking, that slightly increases breathing but still allows conversation. Most pregnant women benefit from about 20 to 30 minutes of such activity at a frequency of 3-5 times per week.
- Monitor blood glucose: Checking glucose levels before and after exercise is important to ensure safety and to adjust activity or snacks if needed. Always stop exercising and consult a healthcare provider if experiencing dizziness, unusual fatigue, or contractions.
Medication Treatment
Some women may require medication even after following dietary and exercise guidelines. When lifestyle measures alone do not achieve glucose targets, insulin injections are a common and reliable treatment for gestational diabetes.
It is particularly important to learn and fully master the procedure under the detailed guidance and demonstration of healthcare professionals before attempting to perform it independently. Under no circumstances should you adjust the type or dosage of insulin on your own. Additionally, continuous blood glucose monitoring is essential throughout the treatment period.
Sinocare’s BGM Blood Glucose Monitor
For expectant mothers with gestational diabetes, blood glucose monitoring is essential. If you're unsure how to choose from the many products on the market, the Sinocare Safe AQ proⅠis a reliable solution. Its features include:
- Precise and Anti-Interference: The test strip utilizes a five-electrode system design and FAD-GDH technology, offering better conductivity and more accurate results. The new hematocrit correction technology enables a wider HCT range (10%-70%), ensuring measurement accuracy for various special populations.
- Larger Storage Capacity: With 500 memory capacity, it helps track blood glucose trends. The device can display overall, pre-meal, and post-meal average glucose values of 7/14/30/90 days as reference.
- Indicator Warnings: The red, yellow, and green indicator tapes clearly show your glucose status.
- Convenient and Fast: Requires only 1 μL of blood and 5s for testing.
- Ketone Alert: When blood glucose measurement results reach ≥13.9 mmol/L, a ketone test reminder will appear on the screen.
Wrapping-Up
How to manage gestational diabetes? It requires consistent monitoring, a balanced diet, safe exercise, and medical care when needed.
With the right tools, such as Sinocare’s Safe AQ pro I, expectant mothers can track glucose in real time and respond promptly to changes. Hope this product will accompany you in safeguarding the health of both you and your baby.
Visit our website now to get one, no matter for a healthy diet or exercise for gestational diabetes.
References
[1]The prevalence of gestational diabetes among underweight and normal weight women worldwide: a scoping review. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11266185/ (Accessed: 11 October 2025)
[2]How to check your blood sugar levels. Available at: https://www.diabetes.org.uk/about-diabetes/looking-after-diabetes/blood-sugar-levels (Accessed: 11 October 2025)
[3]Management of Diabetes in Pregnancy: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Available at: https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/47/Supplement_1/S282/153948/15-Management-of-Diabetes-in-Pregnancy-Standards (Accessed: 11 October 2025)
[4]What can I eat with gestational diabetes? Available at: https://www.diabetes.org.uk/living-with-diabetes/eating/gestational-diabetes (Accessed: 11 October 2025)
[5]THE DIABETIC EXCHANGE LIST (EXCHANGE DIET). Available at: https://www.diabetesed.net/page/_files/THE-DIABETIC-EXCHANGE-LIST.pdf (Accessed: 11 October 2025)









Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.