Early Symptoms of Diabetes
The survey shows that ¼ of diabetic patients do not know that they have diabetes at an early stage. Diabetes has different types, especially Type 2 diabetes. The early symptoms of Type 2 diabetes are not obvious, and are more complicated than Type 1. (In Type 1 diabetes, the human body cannot produce insulin. It is sometimes called juvenile diabetes, It mostly occurs in children and adolescents, but can also occur. At any age.) With the delay of time, when the symptoms become more and more obvious, at this time diabetes has entered a relatively serious stage, How do we simply judge that we are already in the early stage through some symptoms? Is diabetes in early stages?
Both types of diabetes have some of the same telltale warning signs.
- If there are more than 2 of the following signs, it is best to see a doctor for further evaluation. Common symptoms and signs of diabetes include:
- Excessive thirst
- Excessive hunger
- Blurred vision
- Frequent urination (getting up in the toilet at night ≥ 3 times)
- Fatigue (especially after meals)
- Feeling irritable
- The wound does not heal or heals slowly

Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes:
Type 2 Diabetes is often a family history; it can occur at any age and is more common in adults; most of the onset is insidious, with relatively mild symptoms, only mild fatigue and thirst, and more than half have no symptoms; some patients have chronic complications, concomitant diseases or Found during physical examination.People who are sedentary have a higher risk of type 2 diabetes. People who are overweight or obese, or those who eat too many sweets and refined carbohydrates, have a significantly higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
People may suffer from type 2 diabetes throughout their lives, and its occurrence is most often related to poor lifestyle.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes, on the other hand, is a disease most commonly seen in childhood, β the pancreas due to a lack of cells.In addition to children, type 1 diabetes can actually occur at all ages of life, especially menopause. The second characteristic of type 1 diabetes is that the onset of the disease is generally more sudden, thirst, drinking more, more urine, more food and fatigue wasting, weight loss and other symptoms are very obvious, some patients first have ketoacidosis. The third characteristic of type 1 diabetes is that insulin treatment will eventually be used without exception, so type 1 diabetes is also known as insulin-dependent diabetes.
Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes:
High blood sugar during pregnancy usually has no symptoms. You might feel a little thirstier than normal or have to pee more often.
Warning Signs of Diabetes Complications:
Signs of type 2 diabetes' complications may include:
- Slow-healing sores or cuts
- Itchy skin (usually around the vaginal or groin area)
- Frequent yeast infections
- Recent weight gain
- Velvety, dark skin changes of the neck, armpit, and groin, called acanthosis nigricans
- Numbness and tingling of the hands and feet
- Decreased vision
- Impotence or erectile dysfunction (ED)
Hypoglycemia:
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, happens when the level of sugar or glucose in your blood drops too low to fuel the body. You might feel:
- Shaky
- Nervous or anxious
- Sweaty, chilly, or clammy
- Cranky or impatient
- Confused
- Lightheaded or dizzy
- Hungry
- Sleepy
- Weak
- Tingly or numb in your lips, tongue, or cheeks
You might notice:
- Fast heartbeat
- Pale skin
- Blurred vision
- Headache
- Nightmares or crying when you sleep
- Coordination problems
- Seizures
Hyperglycemia:
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, causes many of the warning signs of diabetes listed above, including:
- Heavy thirst
- Blurry vision
- Peeing a lot
- More hunger
- Numb or tingling feet
- Fatigue
- Sugar in your urine
- Weight loss
- Vaginal and skin infections
- Slow-healing cuts and sores
- Blood glucose over 180 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl)
Diabetic Coma:
Its official name is hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome (HHNS). This serious complication can lead to diabetic coma and even death with either type of diabetes, though it’s more common in type 2. It happens when your blood sugar gets too high and your body gets severely dehydrated. Symptoms include:
- Blood sugar over 600 mg/dl
- Dry, parched mouth
- Extreme thirst
- Warm, dry skin that doesn’t sweat
- High fever (over 101 F)
- Sleepiness or confusion
- Vision loss
- Hallucinations
- Weakness on one side of your body
Aaron M. Cypess, M.D., Ph.D., M.M.Sc., an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in the United States, reminded: “The longer you do not control blood sugar in time after diabetes, the higher the risk of serious complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, and blindness.” He suggested People with diabetes risk factors should be evaluated regularly. If the above signals have appeared, it is recommended to check the relevant indicators in the hospital.
It is best to know if you have diabetes as soon as possible, because timely treatment is critical.
Detect HbA1c level:
Get your HbA1c (hemoglobin A1c) levels measured. This is a newer test that is being used by some doctors for diabetes. It looks at the hemoglobin (a protein) in your red blood cells and measures how much sugar is attached. The higher the value, the more sugar is attached, which directly correlates to your risk of having diabetes. (After all, diabetes is the heightened prevalence of sugar in the bloodstream.)

- The normal correlation between HbA1c and average blood sugar levels is as follows. An HbA1c of 6 equates to a blood glucose level of 135. An HbA1c of 7 = 170, an HbA1c of 8 = 205, an HbA1c of 9 = 240, an HbA1c of 10 = 275, an HbA1c of 11 = 301, and an HbA1c of 12 = 345.
- In most labs, the normal range for HbA1c is between 4.0-5.9%. In poorly controlled diabetes, it is 8.0% or above, and in well-controlled patients it is less than 7.0%.
- The benefit of measuring HbA1c is that it gives a more reasonable view of what's happening over the course of time. It reflects your average sugar levels over the past 3 months, rather than a simple glucose test which is a one-time measurement of your sugar levels.
- Keep in mind that HbA1c tests aren’t a perfect diagnostic tool for diabetes. Some conditions, like iron deficiency anemia and chronic blood loss, can cause these tests to give misleading results.(WIkihow)
- WHO Announces the Latest Criteria for Diagnosis of Diabetes
The main harm of diabetes lies in chronic complications caused by poor blood sugar control. This means that if people can receive treatments that help control blood sugar, many chronic complications of diabetes can be avoided or at least delayed. Therefore, timely diagnosis and treatment are the key.



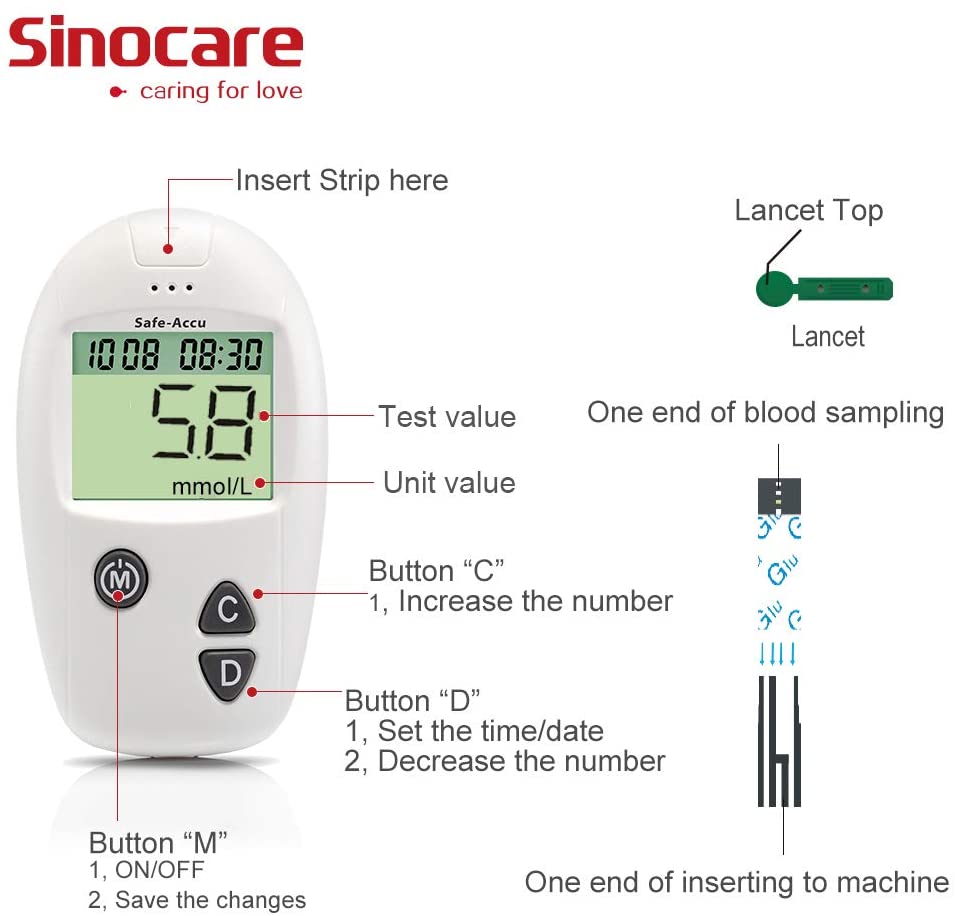




Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.