Living with diabetes requires careful attention to your diet to manage blood sugar levels effectively. With the right balance of nutrients and portion control, you can enjoy flavorful meals while keeping your health in check. In this blog, we'll explore some simple strategies to create a well-balanced plate that caters to the needs of individuals with diabetes.
Three-step combination
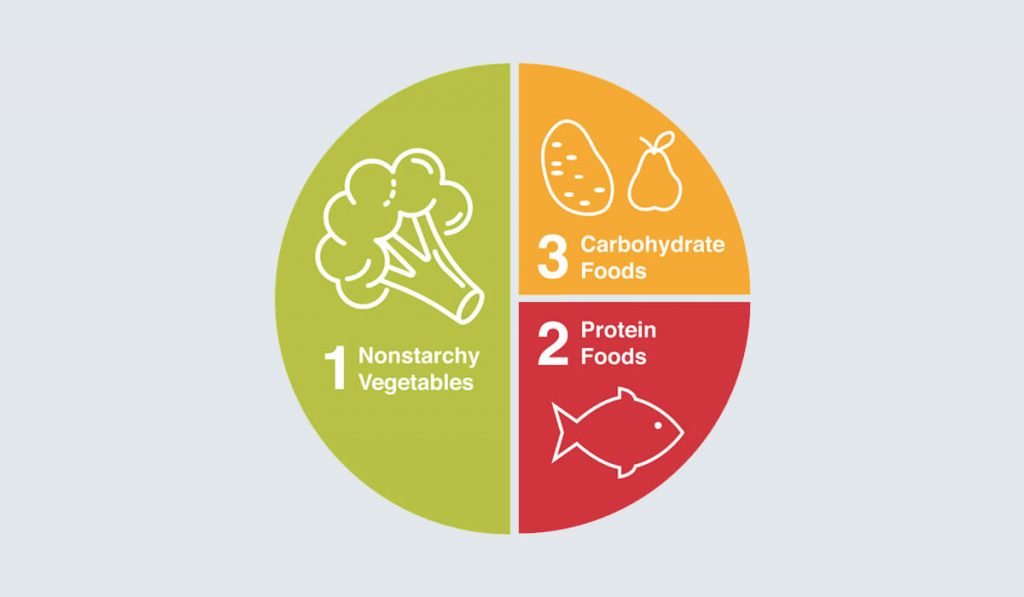
Step One: Find a plate with a diameter of 9 inches (23 centimeters).
Step Two: Divide the plate in half, and then divide one of the halves in half again, just like in the picture.
At this point, we have divided the plate into three parts, which are 1/2, 1/4, and 1/4 of the plate, respectively.
Step Three: Place food in the three divided sections of the plate.
So, what kind of food should we put in each of the three sections of the plate?

Sources: Iowadiabetes
1/2: Non-starchy vegetables
In this section, we'll focus on non-starchy vegetables. However, there's a common misconception that potatoes, lotus roots, and yams are classified as vegetables. But for individuals with diabetes, these have high carbohydrate content and should be considered as staples rather than vegetables.
Non-starchy vegetables are low in calories and rich in dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They can enhance satiety without consuming too many calories and help slow down blood sugar response, preventing rapid spikes after meals.
It's recommended to include at least two or more types of vegetables in each meal. Leafy greens like spinach, bok choy, and kale are excellent options, as well as mushrooms, tomatoes, cucumbers, and eggplants. Aim for a daily intake of around one pound of vegetables.
However, when cooking vegetables, it's best to use methods like stir-frying or cold dressing with minimal oil.

1/4: Grains and starches
This section includes common staple foods such as rice, noodles, and steamed buns. It also encompasses whole grains, potatoes, and starchy vegetables like oats, brown rice, sweet potatoes, potatoes, pumpkins, lotus roots, and yams.
Additionally, legumes rich in starch, such as green beans, lima beans, and red beans, are counted here. When selecting grains, remember that the less processed the food, the lower the glycemic index. Foods with lower glycemic indexes have less impact on blood sugar levels. Furthermore, minimally processed grains contain more protein, minerals, vitamins, and dietary fiber, making them more nutritious. In other words, consuming whole grains directly cooked is much slower in raising blood sugar compared to consuming them ground into powder.

1/4: Meat, poultry, fish, and eggs
This section provides us with essential proteins, which are indispensable for individuals with diabetes.
Excessive fat, especially saturated fat, increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, diabetes patients should try to consume less fatty meats and prioritize leaner options. Moreover, meats from animals with two legs, such as chicken and duck, are preferred over those from animals with four legs, such as pork and beef. Fish with low saturated fat content is the best choice.
When eating meat, opt for lean cuts, and if possible, remove the skin from chicken and duck. If feasible, aim to consume fish 2 to 4 times a week, and you can have one egg per day.

1 Cup of milk
Individuals with diabetes can consume one cup of milk (250-300 milliliters) per day. If drinking cow's milk causes gastrointestinal discomfort, you can opt for yogurt, but be mindful to choose varieties with minimal added sugar.

What about fruits?
You might be wondering why there are no fruits in the picture. When it comes to how individuals with diabetes should select fruits, you're probably already familiar. Fruits with low sugar content and a low glycemic index, such as cherries, strawberries, kiwi, plums, peaches, grapefruits, and cherry tomatoes, can be consumed as snacks between meals when blood sugar levels are stable.
Final thoughts
In conclusion, creating a well-balanced plate for diabetes management doesn't have to be daunting. By following the three-step combination and incorporating non-starchy vegetables, grains and starches, lean proteins, and a serving of dairy, individuals with diabetes can enjoy flavorful and satisfying meals while effectively managing their blood sugar levels. Additionally, being mindful of fruit choices and opting for varieties with low sugar content can further support blood sugar control. With these simple strategies, individuals with diabetes can take charge of their health and enjoy a balanced and nutritious diet that promotes overall well-being.



Commenta
Nota che i commenti devono essere approvati prima di essere pubblicati.
Questo sito è protetto da hCaptcha e applica le Norme sulla privacy e i Termini di servizio di hCaptcha.