Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is vital for overall health, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing it. Fluctuating blood sugar can lead to a range of health issues, including fatigue, mood swings, and long-term complications like nerve damage and cardiovascular disease. However, with some smart strategies and lifestyle adjustments, you can help keep your blood sugar levels in check. Here are 10 clever tricks to aid in stabilizing blood sugar:

1. Facing diabetes
The first step to controlling blood sugar well is to face the fact that you have diabetes. Accepting it and being willing to make changes for better blood sugar control is crucial.
2. Learn about diabetes
Understanding diabetes is key to navigating the path of blood sugar control efficiently. Seek knowledge about diabetes through reputable sources such as attending health lectures at hospitals, reading books on diabetes management, or consulting the latest diabetes-related guidelines if interested.
3. Set your blood sugar control goals
Do not envy others with better blood sugar control; each case is different, and goals may vary. If diagnosed with diabetes (non-pregnancy), the primary goal is to control blood sugar within the target range for diabetics: fasting 4.47mmol/L, postprandial 2-hour blood sugar 4.410mmol/L.
Blood sugar isn't necessarily better the lower it is, nor is it better the faster it decreases. If your blood sugar is currently high, adhere to the doctor's treatment plan, aiming for precise and steady blood sugar control.
4. Have a regular doctor
Many people prefer to see specialists, believing that authoritative experts will have better treatment plans. While specialists do have more experience, appointments are harder to secure, and they have countless patients to attend to each day, making it challenging to receive detailed answers to many questions.
Diabetes is a chronic condition, and anomalies are inevitable. Regularly visit specialists' clinics, such as during the initial diagnosis of diabetes or when medication adjustments are necessary.
For routine check-ups, visit a general practitioner. Choose a fixed doctor who will better understand your condition and provide more help and advice!
5. Learn the correct way to monitor blood sugar
If you have diabetes, monitoring blood sugar is indispensable. It's the most direct and effective way to gauge whether your blood sugar control is on track.
Monitoring blood sugar involves not only mastering the correct operation of the blood glucose meter but also understanding the suitable frequency of blood sugar monitoring for you. Record your blood sugar levels and corresponding sugar control measures such as diet and exercise to facilitate analysis of blood sugar level changes.
6. Maintain regular sleep patterns
Diabetes is an endocrine metabolic disease. Irregular sleep patterns can affect hormone fluctuations. Since diabetic individuals may have varying degrees of pancreatic dysfunction, they may not be able to counteract these hormone changes, leading to more challenging blood sugar control.

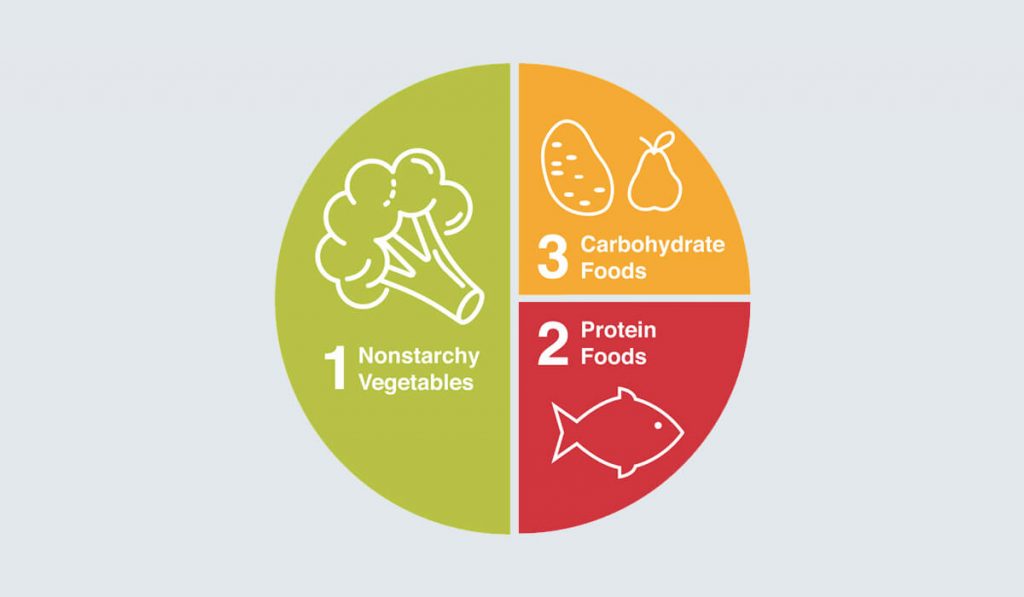
7. Watch what you eat
Watching what you eat doesn't mean you can't eat; it means controlling food quantity. Of course, avoid sweets, beverages, candies, and similar items in the absence of hypoglycemia.
Furthermore, learn to eat balanced meals. Substitute half or more of the refined grains in your daily diet with slow-digesting, low-blood sugar response foods such as oats, buckwheat, red beans, and kidney beans.
8. Get moving
Cultivate the habit of regular exercise, not only to help lower blood sugar but also to promote physical and mental well-being. Aim to exercise for 30 minutes every day; it doesn't have to be formal exercise. Walking, climbing stairs, or jogging are all acceptable, as long as you can stick to it!

9. Regular check-ups
In addition to self-monitoring blood sugar, schedule regular hospital check-ups to understand your body's indicators.
Blood sugar control is crucial in diabetes, but comorbidities are interrelated. Diabetic patients are more prone to developing other chronic diseases such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and hyperuricemia. Diabetes also has a range of complications. Regular check-ups enable early detection and treatment of problems, preventing them from worsening.
10. Adjust emotions
Fear and worry about diabetes, work, and life stress can leave us physically and mentally exhausted. Negative emotions can also affect blood sugar control.

Final thoughts
In conclusion, stabilizing blood sugar levels is a multifaceted endeavor that requires dedication, education, and lifestyle adjustments. By facing diabetes head-on, learning about the condition, and setting realistic blood sugar control goals, individuals can empower themselves to take charge of their health. By incorporating these ten clever tricks into daily life, individuals with diabetes or those at risk can enhance their overall well-being and reduce the risk of complications associated with fluctuating blood sugar levels.







Commenta
Nota che i commenti devono essere approvati prima di essere pubblicati.
Questo sito è protetto da hCaptcha e applica le Norme sulla privacy e i Termini di servizio di hCaptcha.