Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) results from hemoglobin being wrapped in blood sugar. The amount of glucose combined from hemoglobin is directly proportional to the total glucose content in the blood system. As such, the higher the blood sugar level, the higher the HbA1c level. Due to the fact that red blood cells boast a lifespan of 120 days, doctors can check the average blood sugar level for a period of 2 to 3 months.
It is significant for people with diabetes to conduct the HbA1c test in that the higher the HbA1c level, the greater the risk of diabetic complications.
What is the difference between glycosylated hemoglobin test and blood sugar test?
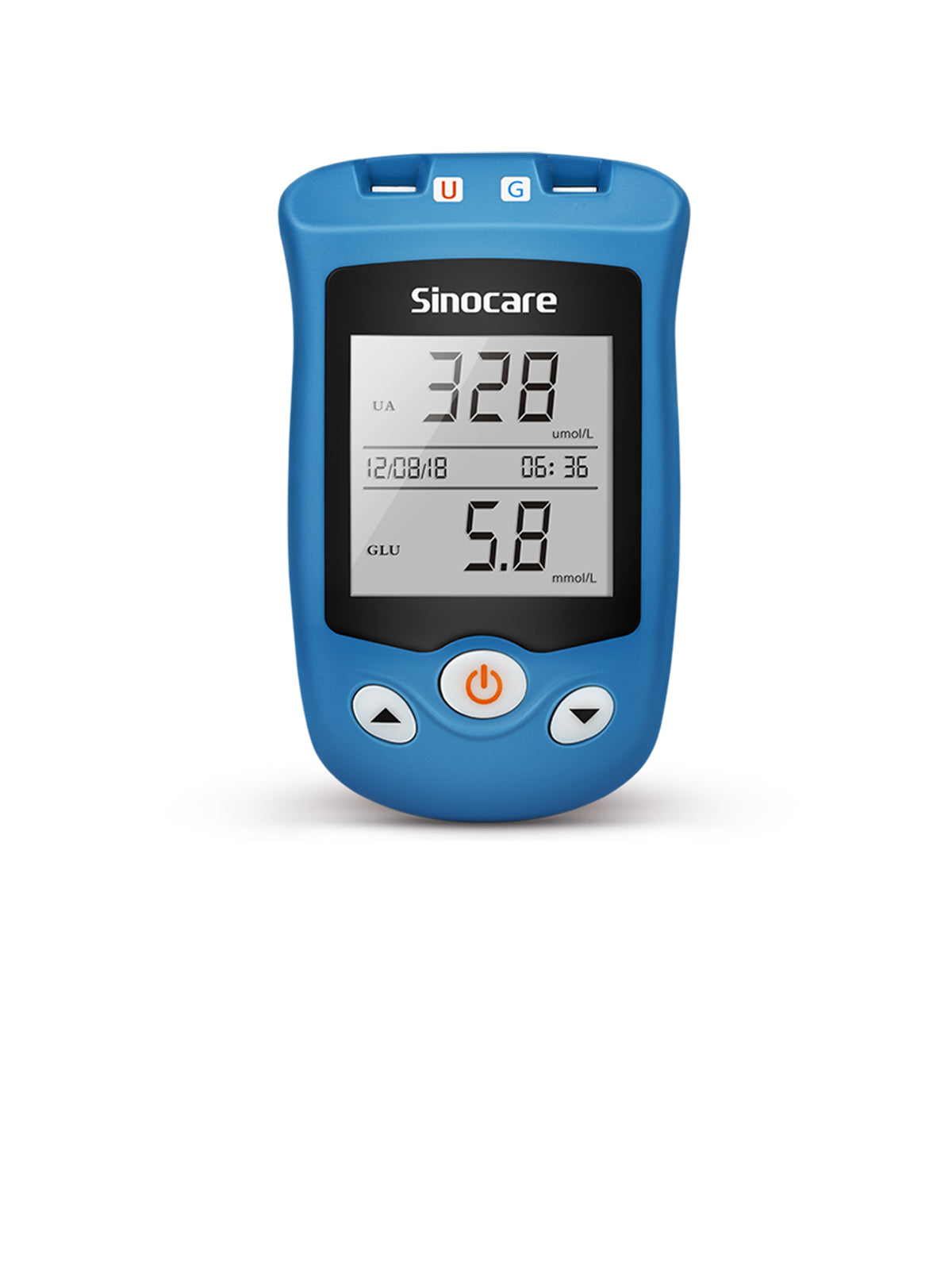
There is no need for people to do HbA1c test without eating. It can reflect the average blood glucose level of 2 to 3 months and is a more reliable test for evaluating the effect of long-term blood sugar control. This means that the level of glycosylated hemoglobin is hard to produce daily fluctuations caused by the influence of stress and disease. However, the blood glucose test only represents the blood glucose concentration in the blood at the time.
What is the normal value of glycosylated hemoglobin?
It's common for people with diabetes to see that HbA1c levels reach no more than 7%. But doctors should tailor individual goals for patients. The HbA1c value fail to reflect a specific diabetic complication, indicating any level of HbA1c test value can allow the complication to happen. It's surely better for the glycosylated hemoglobin test value to be close to the normal value.
What are the benefits of lowering glycosylated hemoglobin?
Studies have shown that if the HbA1c level of diabetic patients is reduced by 1%, complications of the eyes, kidneys and nervous system will be reduced by 25%.
In addition, when HbA1c levels of type 2 diabetic patients decrease 1%, it's possible to reduce the happening of cataracts by 19% and heart failure by 16%. Therefore, lower HbA1c levels mean lower average blood glucose levels, so is the risk of complications.
The targeted people to perform the glycosylated hemoglobin test:
- Type 2 diabetic patients should perform this test at least once a year.
- Some patients may need more frequent HbA1c examinations, especially patients whose treatment plan has changed recently, or when medical staff need to monitor the patient's condition more frequently.
- For people who are not suffering from diabetes, experts suggest that people who are over 45 years old should consider glycosylated hemoglobin test, especially if they are overweight or obese.
The limitations of the glycosylated hemoglobin test:
Although the HbA1c test is generally reliable and has been widely used, the test may not be accurate in the following situations:
- The amount of hemoglobin decreased due to excessive blood loss;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- Hemoglobin gene mutation or abnormal hemoglobin: common in African Americans, people living in Mediterranean or in Southeast Asia;
- Recent history of blood transfusion or other forms of hemolytic anemia;
- Pregnancy.
How to control glycosylated hemoglobin levels?
People are able to control HbA1c levels by adopting a healthy lifestyle, which is beneficial to reducing long-term diabetic complications. To reduce the level of glycosylated hemoglobin, people need to follow the steps:
Patients with diabetes and prediabetes need to consume low-calorie and nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, dietary fiber, high-quality protein and appropriate amounts of monounsaturated or polyunsaturated fatty acids. Meanwhile, saturated fatty acids, carbohydrates and ultra-processed foods should be restricted.
For example, eating whole wheat bread and brown rice instead of white bread and white rice will help reduce blood sugar spikes after meals. If necessary, people can consult a dietitian for food selection and diet planning.
- Regular exercise:
With continuous exercise, blood sugar will be transferred from the blood to the cells to generate energy for the body, thereby reducing blood sugar levels. In addition, exercise will increase the body's sensitivity to insulin.
People should incorporate physical activity into their daily lives. For people without diabetes, exercise will help prevent prediabetes and type 2 diabetes while for people who already have diabetes, exercise can help maintain good blood sugar level. American Diabetes Association points out that people should exercise at least 5 days a week, 30 minutes a day.
- Regular monitoring:
It is generally recommended that glycated hemoglobin should be monitored for 2-3 months to assess the control of diabetes. However, the HbA1c test cannot completely replace blood glucose monitoring. For example, patients treated with insulin and other drugs need regular blood glucose monitoring to ensure that blood sugar is not too low.







Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.