Accurate blood glucose monitoring is the foundation of effective diabetes management. For both healthcare professionals and people managing diabetes at home, reliable readings are essential for making informed decisions about medication, diet, and daily activity. As a result, many users—especially first-time users—often ask: Do blood sugar monitors need calibration, and how can accuracy be ensured?
Understanding Calibration in Blood Glucose Monitoring
Calibration refers to the process of adjusting or verifying a medical device so that its readings align with a known reference standard, usually laboratory values. In traditional blood glucose monitoring, this verification has commonly been done using a control solution—a liquid with a predefined glucose concentration.
When the control solution is applied to a test strip, the displayed result should fall within the acceptable range printed on the test strip vial. This confirms that both the meter and the strips are functioning properly.
In earlier generations of blood glucose meters, users were often required to manually “code” the device by entering a number or inserting a code chip to match each new batch of test strips. Incorrect coding or skipped steps could lead to significant measurement errors and potentially inappropriate treatment decisions. While most modern meters have eliminated this step, understanding the verification process remains an important part of basic health literacy.
How to Check the Accuracy of a Blood Sugar Monitor
Although most modern blood glucose meters no longer require manual calibration, users can still perform an accuracy check to ensure reliable performance. A standard control test typically involves the following steps:
- Prepare the Meter: Make sure the device is clean, properly stored, and powered with fresh batteries.
- Use Control Solution: Apply a drop of the manufacturer-recommended control solution to a test strip instead of blood.
- Compare the Results: Confirm that the reading falls within the range listed on the test strip container.
- Repeat When Necessary: Accuracy checks are recommended when opening a new box of test strips, after dropping the meter, or when readings do not match physical symptoms.
This process helps verify accuracy without requiring technical calibration by the user.
Simplifying Monitoring with Sinocare No-Coding Technology
As a global leader in biosensor technology, Sinocare has focused on simplifying blood glucose monitoring while maintaining high accuracy standards. Most Sinocare blood glucose meters feature No-Coding technology, which automatically recognizes test strips and eliminates the risk of manual coding errors—historically one of the most common causes of inaccurate home readings.
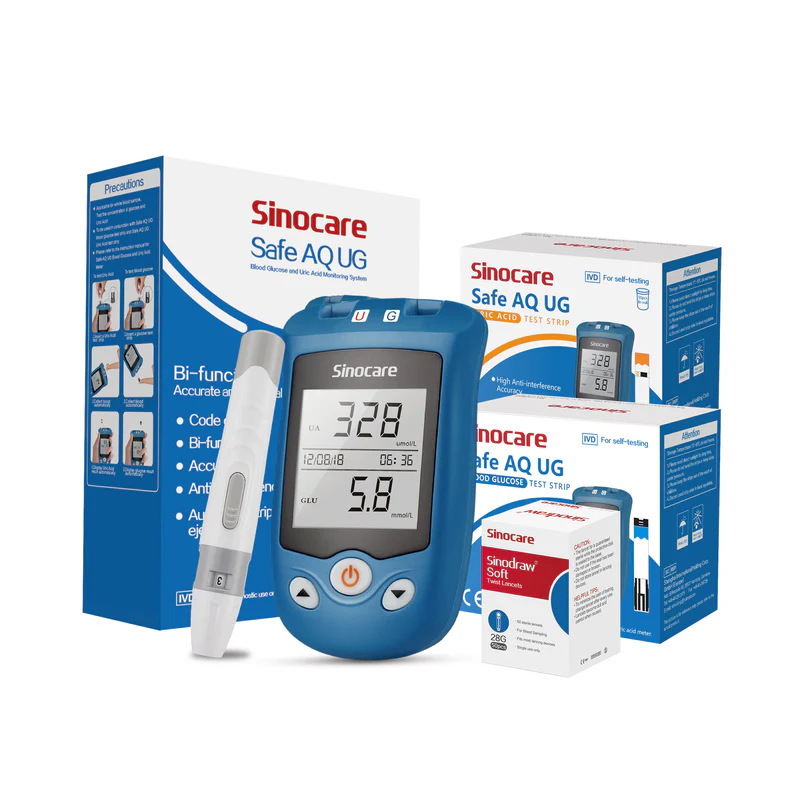
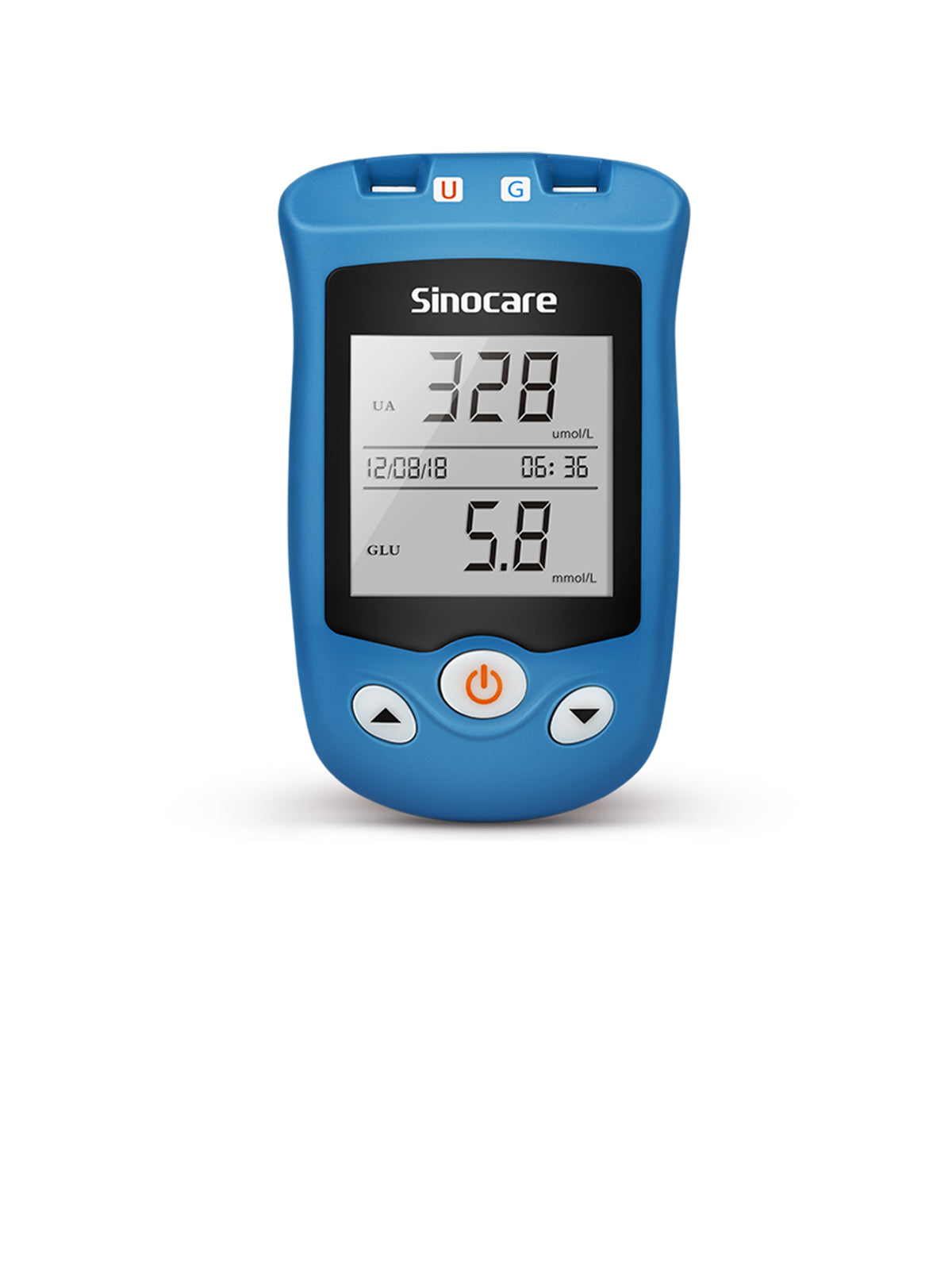
Using a Sinocare blood sugar monitor is straightforward: insert the test strip, apply a small blood sample, and receive results within seconds. For optimal accuracy, it is important to use compatible Sinocare test strips. Devices such as the Sinocare Safe AQ UG Blood Glucose Uric Acid Meter combine fast measurement, precise results, and a clear high-contrast LCD design for convenient daily use.
Choosing a Reliable Blood Sugar Monitor
An effective blood sugar monitor should balance accuracy, ease of use, and long-term reliability. By integrating advanced biosensor technology with automated internal calibration, Sinocare blood glucose meters help reduce user error while delivering consistent results.
In daily diabetes management, where even small measurement differences matter, choosing a monitor that supports accuracy without adding operational complexity can make blood glucose monitoring safer, simpler, and more sustainable over time.









Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.